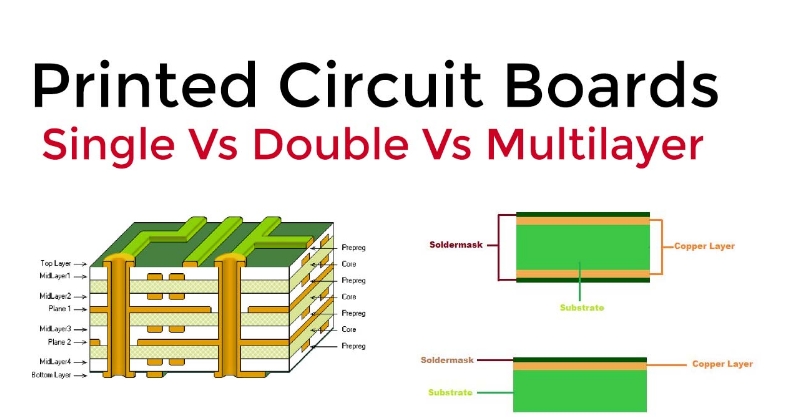
Multilayer PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) and single-layer PCBs differ in their design complexity and applications. Here are the key distinctions between the two:

Single-Layer PCB:
1.Structure:
Consists of a single layer of substrate material (usually fiberglass-reinforced epoxy).
Conductive copper traces are present on only one side of the board.
2.Applications:
Simple electronic devices with basic circuitry.
Cost-sensitive applications.
Prototyping and low-complexity projects.
3.Advantages:
Lower cost to manufacture.
Easier to design and fabricate.
Suitable for basic circuits with minimal components.
4.Limitations:
Limited routing space, which can restrict complexity.
Larger size due to limited space for traces.
Multilayer PCB:
1.Structure:
Consists of multiple layers of substrate material (usually four or more layers).
Conductive copper traces are sandwiched between the layers, and vias connect the traces between layers.
2.Applications:
Complex electronic devices with advanced functionality.
High-performance applications (e.g., computers, smartphones, medical devices).
Products with miniaturized components.
3.Advantages:
Greater design flexibility and complexity.
Smaller size due to increased routing space.
Improved signal integrity and reduced electromagnetic interference (EMI).
4.Limitations:
Higher manufacturing cost.
More complex design and debugging.
Considerations:
Cost: Single-layer PCBs are generally more cost-effective, making them suitable for simpler applications with budget constraints.
Complexity: For complex circuits and densely packed components, multilayer PCBs are essential to provide sufficient routing space.
Space Efficiency: Multilayer PCBs allow for more compact designs, which is crucial in applications where space is limited.
Signal Integrity: Multilayer PCBs can provide better signal integrity and reduced EMI due to the ability to separate power and ground planes.
In summary, the choice between a single-layer and multilayer PCB depends on the specific requirements of the electronic device, including the complexity of the circuit, available space, performance demands, and budget constraints.