The term "DHI PCB" is not a widely recognized or standard term in the field of printed circuit boards (PCBs). It is possible that it is a specific term used in a particular context or by a specific company or organization. However, without more information or context, it is challenging to provide a comprehensive guide to the DHI PCB definition.
In the PCB industry, various terms and abbreviations are used to describe different types of PCBs, materials, manufacturing processes, and applications. Some commonly used terms related to PCBs include:
1.PCB (Printed Circuit Board): A PCB is a flat board that mechanically supports and electrically connects electronic components using conductive tracks, pads, and other features etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate.
2.FR-4: FR-4 is a common material used for PCB substrates. It is a flame-retardant, woven glass-reinforced epoxy laminate that provides excellent electrical insulation and mechanical strength.
3.SMT (Surface Mount Technology): SMT is a method of assembling electronic components directly onto the surface of a PCB, as opposed to through-hole mounting.
4.HDI (High-Density Interconnect): HDI PCBs have high-density circuitry with microvias, blind vias, and buried vias, allowing for more compact designs and improved signal performance.
5.Flex PCB (Flexible Printed Circuit Board): Flex PCBs are made of flexible plastic materials, enabling them to bend or twist to fit into unique form factors or three-dimensional designs.
6.Rigid-Flex PCB: Rigid-flex PCBs combine elements of both rigid and flexible PCBs, allowing for complex, space-saving designs.
If you have more context or specific information about the "DHI PCB" term you are referring to, please provide additional details, and I will do my best to assist you further.
Unveiling the Advanced World of HDI PCBs: Revolutionizing Electronic Designs
In the dynamic landscape of electronic manufacturing, staying at the forefront of technological advancements is paramount. This article aims to augment your understanding by incorporating key terms such as HDI PCBs, HDI boards, and other related concepts that are crucial for navigating the competitive terrain of the industry.
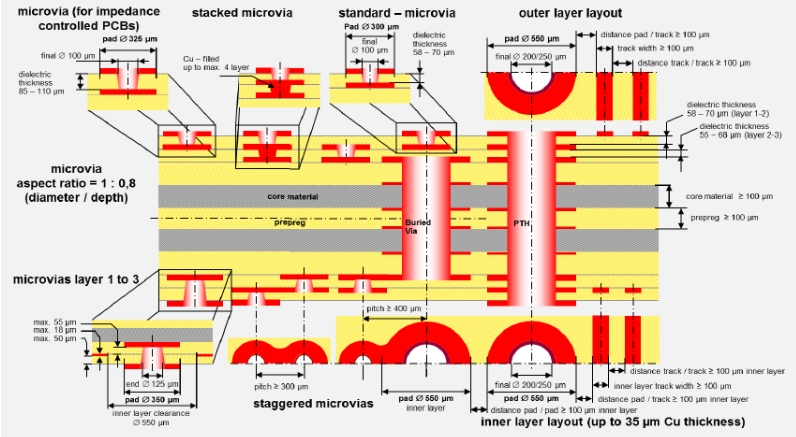
1. Exploring HDI PCBs:
High-Density Interconnect (HDI) PCBs stand as a pinnacle in modern electronic design. Understanding the intricacies of HDI boards, which include features like laser drills, sequential lamination, and a higher layer count, is essential for harnessing the full potential of electronic components.
2. The Significance of PCB Designs in HDI Technology:
HDI technology relies heavily on precise PCB designs. The lamination process, pin count considerations, and achieving a favorable aspect ratio are integral components of creating sophisticated multilayer PCBs with high wiring density.
3. Sequential Lamination and Manufacturing Processes:
Delving into sequential lamination unveils the sophisticated steps involved in the manufacturing processes of HDI PCBs. This includes intricate details like layer stacking, laser drills for microvias, and optimizing wiring density per unit area.
4. Multilayer PCBs and Wiring Density Optimization:
The evolution of electronic devices demands higher wiring density per unit area. Multilayer PCBs, a hallmark of HDI PCB design, allow for a significant increase in wiring density, resulting in more functionality packed into fewer square inches.
5. Aspect Ratio and Pin Count Considerations:
The aspect ratio, defined as the ratio of the board thickness to the diameter of the drilled hole, becomes a critical factor in achieving optimal performance in HDI PCBs. Pin count considerations further emphasize the need for precision in HDI PCB design.
6. Deciphering HDI Technology for Innovation:
HDI technology, which stands for High-Density Interconnect, epitomizes the pursuit of higher wiring density, miniaturization, and enhanced functionality. It opens doors to a realm where electronic designs are not just components but intricate systems optimized for the modern era.
In conclusion, enriching your understanding of HDI PCBs involves embracing concepts like sequential lamination, laser drills, layer count optimization, and the significance of aspect ratio. As the industry evolves, so does the demand for higher wiring density and innovative manufacturing processes, making HDI technology a cornerstone for those aiming to push the boundaries of electronic design.
Get more knowledge about HDI PCB Definition please refer to Rigaopcb:https://www.rigaopcb.com/