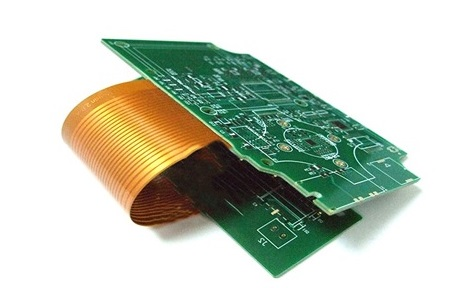
A Rigid Flex PCB (Printed Circuit Board) is a hybrid circuit board that incorporates elements of both rigid and flexible PCBs within a single design. It is a combination of rigid and flexible substrates that are laminated together to create a single, unified board. Rigid Flex PCBs provide a versatile solution for electronic designs that require a combination of the structural stability of rigid boards and the flexibility offered by flexible circuits.

Here are key differences between Rigid Flex PCBs and traditional rigid or flexible PCBs:
1. Combination of Rigid and Flexible Sections:
Rigid PCBs: These are made of a solid, inflexible substrate material, such as FR-4, providing structural support to electronic components.
Flexible PCBs:These are made of flexible materials, such as polyimide, allowing the board to bend or conform to a specific shape.
Rigid Flex PCBs:Combine rigid and flexible sections within the same board. The rigid sections provide stability for components and connectors, while the flexible sections allow the board to bend or fold as needed.
2. Space and Weight Savings:
Rigid PCBs:Can be bulky and may not be suitable for designs with limited space or those requiring flexibility.
Flexible PCBs:Offer space and weight savings but may lack the structural support needed in certain applications.
Rigid Flex PCBs:Provide a compromise by offering the structural integrity of rigid boards and the flexibility of flexible circuits, allowing for more compact and lightweight designs.
3. Reduced Interconnects:
Rigid PCBs:Interconnects are typically achieved using connectors and cables.
Flexible PCBs:Allow for direct routing in three dimensions, reducing the need for connectors.
Rigid Flex PCBs:Combine the benefits of direct routing in flexible sections with the stability of rigid sections, minimizing the use of external connectors and cables.
4. Complex Designs:
Rigid PCBs:Suited for simple designs with straightforward geometries.
Flexible PCBs:Ideal for applications where bending or shaping is required.
Rigid Flex PCBs:Enable the integration of complex designs, making them suitable for applications with dynamic form factors or those requiring reliability in harsh conditions.
5. Reliability:
Rigid PCBs: Known for their stability and durability.
Flexible PCBs:Can be prone to damage if bent or flexed excessively.
Rigid Flex PCBs:Combine the reliability of rigid sections with the flexibility needed in certain applications, providing a balance between stability and adaptability.
In summary, Rigid Flex PCBs offer a flexible and space-efficient solution, making them suitable for applications where a combination of structural integrity and flexibility is required, such as in aerospace, medical devices, and other complex electronic systems.