Rigid-Flex PCB, short for rigid-flexible printed circuit board, represents a hybrid circuit board that incorporates both rigid and flexible board technologies. Unlike traditional rigid PCBs, which are inflexible and limit the design possibilities, Rigid-Flex PCBs enable three-dimensional configurations and intricate bending, allowing for a more efficient use of space within electronic devices.
Rigid Sections
The rigid sections of a Rigid-Flex PCB are composed of solid, inflexible materials such as FR4, similar to those used in traditional rigid PCBs. These sections provide structural support to the overall board and house components that require a stable platform.
Flexible Sections
The flexible sections, on the other hand, are made from polyimide or similar flexible materials. These sections allow the PCB to bend and twist, making it ideal for applications where space optimization and dynamic shapes are crucial.
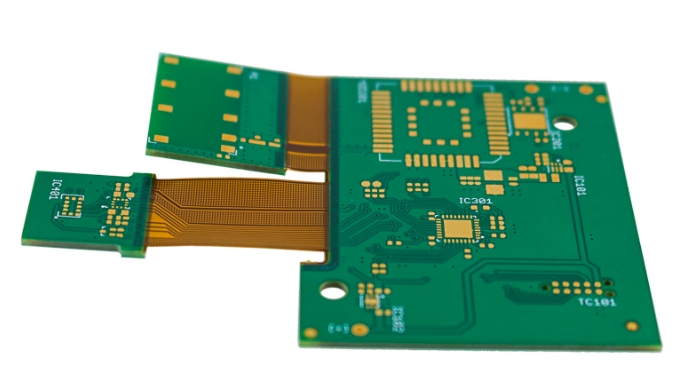
Rigid-Flex PCBs find applications in a wide range of industries, thanks to their unique combination of rigidity and flexibility. Some notable applications include:
1.Aerospace and Defense
In aerospace and defense applications, where weight reduction, space optimization, and reliability are paramount, Rigid-Flex PCBs are increasingly preferred. They can conform to the shape of the device, offering a compact and lightweight solution.
2.Medical Devices
Medical devices often require intricate designs to fit within the constraints of the human body. Rigid-Flex PCBs provide the flexibility needed for such designs while maintaining the structural integrity required for reliable performance.
3.Consumer Electronics
In the consumer electronics sector, especially in smartphones and wearable devices, Rigid-Flex PCBs enable the creation of compact, lightweight, and aesthetically pleasing products. They contribute to the slim form factors and enhanced functionalities demanded by modern consumers.
The adoption of Rigid-Flex PCB technology comes with a multitude of advantages, making it a preferred choice for various applications:
1.Space Optimization
Rigid-Flex PCBs allow designers to maximize space utilization within electronic devices. The flexibility of these boards enables them to fit into unconventional shapes and tight spaces, contributing to overall product miniaturization.
2.Improved Reliability
The elimination of connectors and cables, common sources of failure in electronic devices, enhances the reliability of Rigid-Flex PCBs. The integrated design reduces points of failure, leading to improved durability and performance.
3.Simplified Assembly
The integration of rigid and flexible sections in a single board streamlines the assembly process. Fewer components and connections translate to reduced assembly time, lower labor costs, and improved overall efficiency in manufacturing.
The choice between Rigid-Flex and rigid PCBs often boils down to cost considerations. Understanding the factors influencing the cost of each type is crucial for making informed decisions in electronic design projects.
1.Material Costs
Rigid-Flex PCBs typically involve a combination of flexible and rigid materials. Analyzing the cost difference in these materials sheds light on the overall expenses and cost-effectiveness.
2.Design Complexity
The complexity of the design plays a significant role in cost determination. Rigid-Flex PCBs offer more design freedom, allowing for three-dimensional configurations. Examining how design intricacies impact manufacturing costs is essential.
3. Assembly and Testing
The assembly and testing processes for Rigid-Flex PCBs may differ from those of rigid PCBs. Understanding the nuances in assembly techniques and testing requirements helps in evaluating the cost implications of each approach.
4.Unveiling the Characteristics of Rigid-Flex PCB
Rigid-Flex PCBs exhibit unique characteristics that make them suitable for specific applications. Exploring these characteristics provides a comprehensive understanding of the advantages and considerations associated with this technology.
5. Flexibility and Space Optimization
The flexible portions of Rigid-Flex PCBs allow for intricate bending, facilitating space optimization within electronic devices. Examining how this flexibility contributes to space-efficient designs is crucial for designers and engineers.
6.Reliability and Durability
Understanding the reliability and durability of Rigid-Flex PCBs is essential for applications requiring repeated flexing or exposure to challenging environments. Exploring the materials and manufacturing techniques contributes to assessing their long-term performance.
7.Weight Reduction Benefits
Rigid-Flex PCBs often contribute to overall weight reduction in electronic devices. Evaluating the impact on weight and its significance in various industries helps in making informed decisions during the design phase.
The manufacturing process of Rigid-Flex PCBs involves a combination of techniques to achieve the desired flexibility and reliability. Understanding these manufacturing processes provides insights into the challenges and innovations in producing Rigid-Flex PCBs.
1. Layer Lamination and Bonding
The layer lamination process in Rigid-Flex PCB manufacturing involves bonding flexible and rigid layers together. Delving into the methods and materials used in this process sheds light on the structural integrity of the final product.
2.Drilling and Plating
The drilling and plating processes in Rigid-Flex PCB manufacturing require precision to maintain the integrity of flexible portions. Examining the techniques used in drilling and plating contributes to understanding the challenges and quality control measures.
3.Quality Control Measures
Ensuring the reliability of Rigid-Flex PCBs involves stringent quality control measures. Exploring the testing and inspection methods implemented during and after manufacturing provides insights into the steps taken to guarantee the final product's functionality.
In conclusion, exploring Rigid-Flex PCBs involves a comprehensive analysis of cost factors, understanding unique characteristics, and delving into the intricacies of the manufacturing process. This knowledge equips designers and engineers with the information needed to make informed decisions in adopting Rigid-Flex PCB technology for their electronic applications.